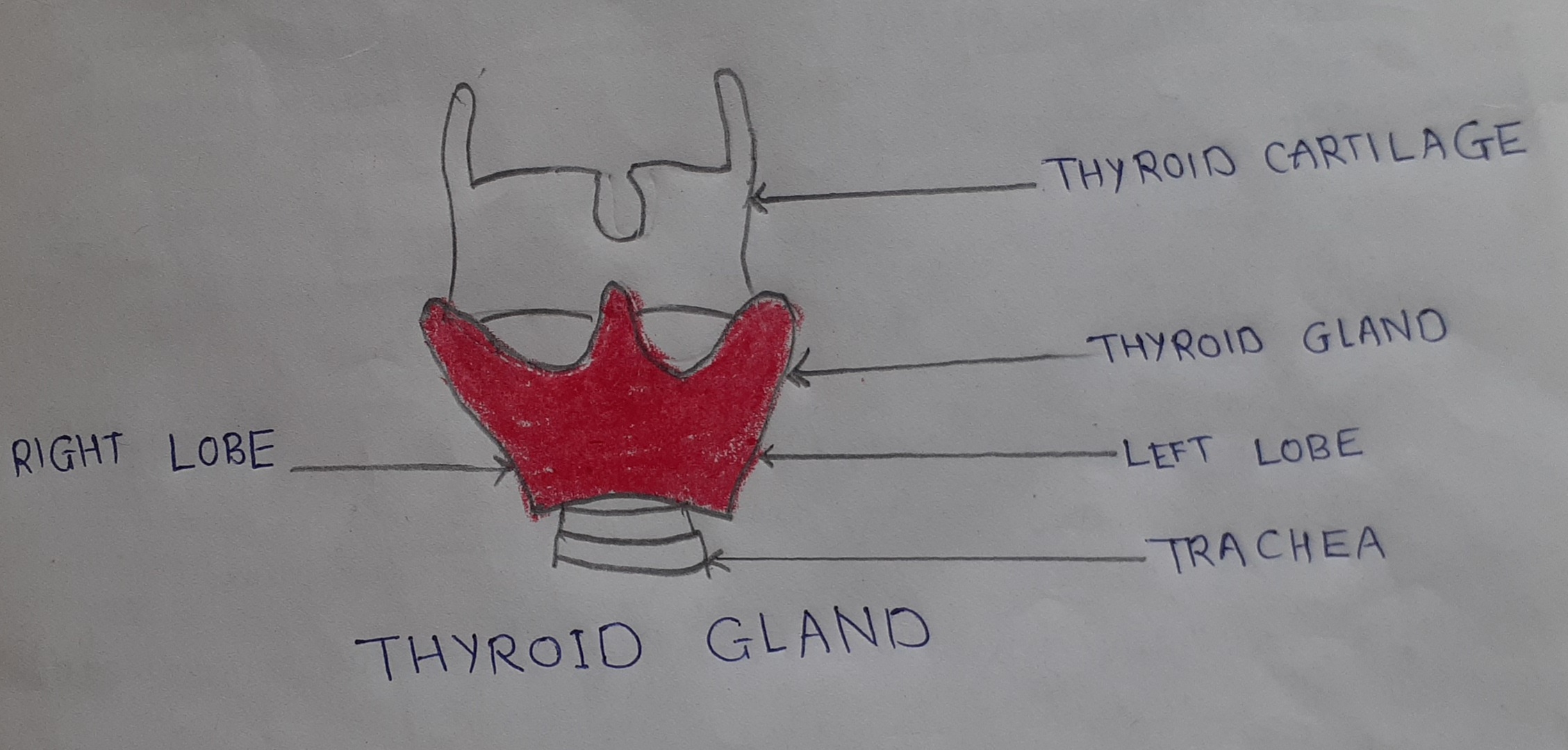
The thyroid gland weighs approximately 20 grams. It is situated in the lower neck of both sides of the trachea. The thyroid gland consists of many follicles. The thyroid gland secretes tyrosine ( T4) triiodothyronine (T3). Major part of the thyroid hormone secreted is T4 which lasts longer than T3. But active T3 is 3,4 times more potent than T4. The thyroid hormone moves in blood partly free and partly bound to plasma proteins.T4 is bound to thyroxine binding globulins (TBG) thyroxine binding prealbumin(TBPA) and albumin. T3 is bound less firmly and the proportions of T3 is 8 to 10 times more than that of T4.
Control of thyroid gland
The TSH or Thyroid stimulating hormone is secreted by anterior pituitary and stimulates thyroid growth, increase gland activity. TSH is regulated by Thyrotropin releasing hormone (from hypothalamus).
Serum T3 T4 inhibit TSH secretion which in turn inhibits secretion of T3, T4.
Thyrotoxicosis or hyperthyroidism
Symptoms increased pulse especially fast asleep pulse. Therearepalpitation. . Increased heart rhythms like atrial fibrillation. Heart failure. Weight loss with increased appetite. Excessive sweating.
Tests
Radioactive iodine uptake T3 T4 Radioactive thyroid scan USG thyroid
Treatment
Anti thyroid drugs
Removal of thyroid by radioactive iodine or surgery
Hypothyroidism
Deficiency of thyroid hormone resulting in slowing of bodily activity can be due to inadequate TRH Secretion or due to low functioning pituitary. It can be due to iodine deficiency.
Symptoms
Tired, lethargic, depression, puffy face, hair loss, dry skin, constipation, impaired memory and concentration, hoarse voice, weight gain inspite of loss of appetite.
Diagnosis
T3, T4, TSH in blood
Treatment
Levothyroxine